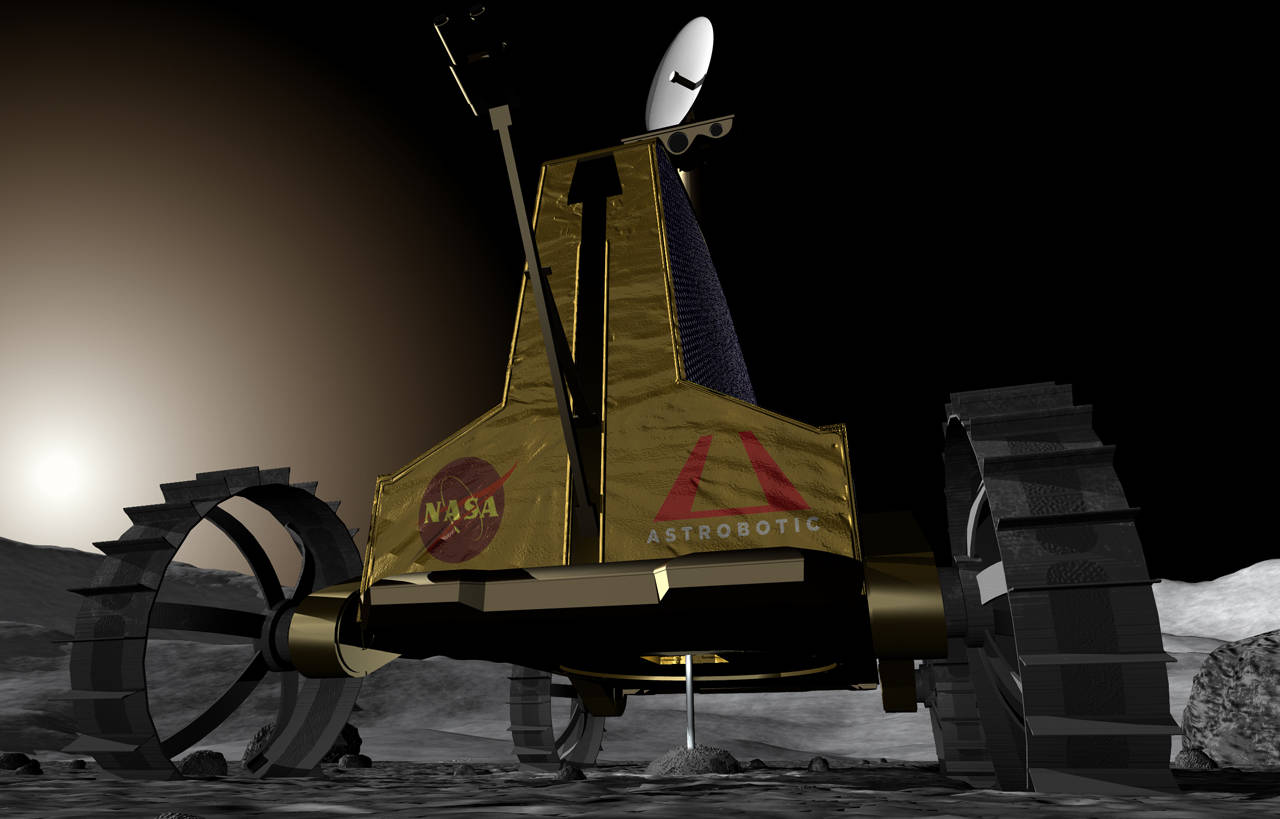

The company Astrorobotic Technology is planning on sending a robot rover to the Moon on a mission to look for water on its north pole. This will be a three-year mission during which it will prospect the soil for water ice and also methane or other potential resources.
Polaris is one of two Moon rovers presently under development by Astrobotic in competition for the Google Lunar X Prize.
This is an X-Prize competition that offers 30 million dollars in awards in total, for which 20 million is awarded to the winner. The winner is the team that is able to safely land a robot on the surface of the Moon, have it travel 500 meters over the lunar surface, and then send videos, photos, and data back to Earth.
Polaris Rover Specifications:
Operating Environment: Lunar Poles and high latitudes
Rover Mass: 150kg
Payload Mass: 80kg
Average Power: 250W (800W peak)
Drive Speed: 30 cm/s
Dimensions (LxWxH): 2.4 x 1.7 x 2.6m
Features: Night Survival, Autonomous Roving, Passive Thermal Control, Skid-Steer, Passive Rocker Suspension, Composite Chassis, 3D laser scan mapping, 3D-HD cameras, 4x telephoto zoom camera, Direct to Earth Communication
Astrobotic has booked a Falcon 9 launch by SpaceX, to send its spacecraft and robotic robot to the Moon in October of 2015.
Below two videos, with one presenting the Polaris Rover and the other a time lapse of its assembling process at Astrororobotic Technology.
_______________
Astrobotic Technology/
______________________________









![OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. https://chatgpt.com](https://www.illustratedcuriosity.com/files/media/55136/b1b0b614-5b72-486c-901d-ff244549d67a-350x260.webp)
![OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. https://chatgpt.com](https://www.illustratedcuriosity.com/files/media/55124/79bc18fa-f616-4951-856f-cc724ad5d497-350x260.webp)
![OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. https://chatgpt.com](https://www.illustratedcuriosity.com/files/media/55099/2638a982-b4de-4913-8a1c-1479df352bf3-350x260.webp)








