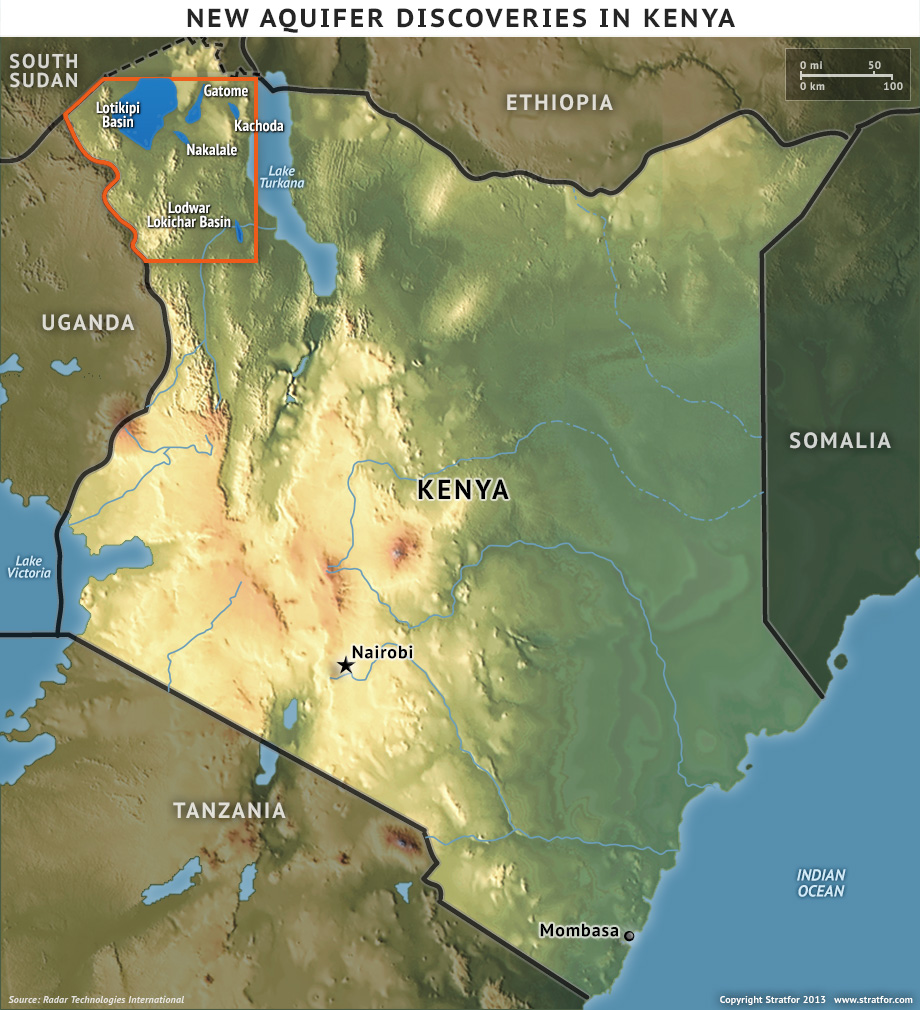
UNESCO has found a previously unknown underground water aquifer reservoir in Kenya. The pool was found more than 300 meters underground and is believed to contain around 200 billion cubic meters of fresh water.
An Enormous Amount of Water
The reservoir has been named Lotikipi Basin Aquifer and its finding could provide nine times the amount of water of all previously known freshwater sources in Kenya. It contains 25 times the volume of Loch Ness lake and this would be enough to supply the entire Kenyan population with water for 70 years.
The hope is now that this newly discovered water source is to be used for both drinking as well as irrigation for crops and thereby possibly spawn a whole new agriculture industry, providing food, and start a virtues circle of investments in the relatively poor country.
It was found by UNESCO and the Kenyan government together with the French company called Radar Technologies International, using a multitude of technologies typically used to locate oil reserves, satellite, radar, geological maps along with seismic techniques.
The Lotikipi aquifer in statistics:
It is approximately 100 km (62 miles) by 66 km (41 miles).
It has a surface area of 4,164 km2.
Contains an estimated 200 billion cubic meters of fresh water.
Contains alone more than 9 times the amount of Kenya’s present water reserves.
Fresh Water Future?
Naturally, the finding is not a total problem solver, but it may become a game changer. Its discovery is certainly a great step towards alleviating Kenya’s immediate problems but it could also move the country onto a new level, to build upon for the future. The amount of water may be abundant, but the need for efficient water treatment, recycle and conservation is as important as ever before.
With fresh water only amounting to a total of 2,5 percent of all water on Earth, the other 97,5 percent being salt water, we can all hope for a future of efficient and cheap salt-water conversion to be available. With several different desalination technologies in development, such as forward osmosis, carbon nanotubes, and biomimetics.
_______________
Strategic groundwater reserves found in Northern Kenya
______________________________









![OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. https://chatgpt.com](https://www.illustratedcuriosity.com/files/media/55136/b1b0b614-5b72-486c-901d-ff244549d67a-350x260.webp)
![OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. https://chatgpt.com](https://www.illustratedcuriosity.com/files/media/55124/79bc18fa-f616-4951-856f-cc724ad5d497-350x260.webp)
![OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. https://chatgpt.com](https://www.illustratedcuriosity.com/files/media/55099/2638a982-b4de-4913-8a1c-1479df352bf3-350x260.webp)








