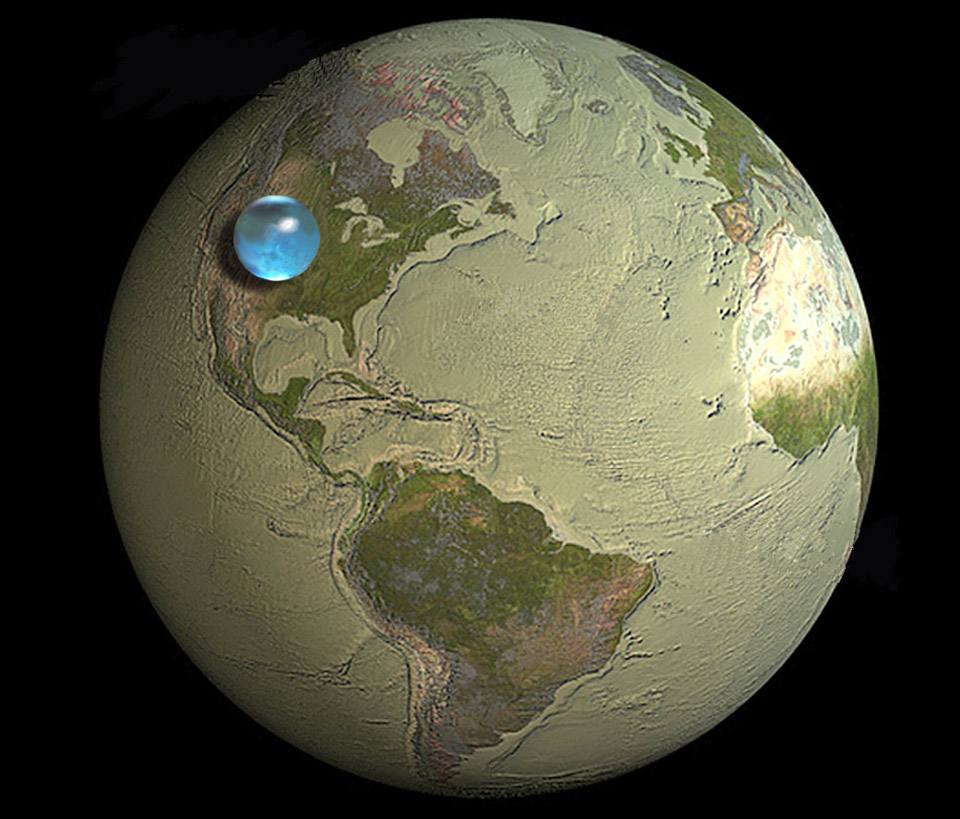
Researchers have found large quantities of fresh water under the seabed, making the total amount of fresh water on Earth a little greater than previously thought.
Found at Continental Shelves
The study was published in the December 5th issue of the scientific journal Nature and reveals that an estimated half a million cubic kilometers of low-salinity water have been found beneath the seabed on continental shelves all around the world.
Dr. Vincent Post from the National Centre for Groundwater Research and Training ( NCGRT ) writes, “The volume of this water resource is a hundred times greater than the amount we’ve extracted from the Earth’s sub-surface in the past century since 1900,”
“Knowing about these reserves is great news because this volume of water could sustain some regions for decades.” “Our research shows that fresh and brackish aquifers below the seabed are actually quite a common phenomenon,” he adds.
Ancient Water
The freshwater aquifers were formed in a process that has lasted during the past hundreds of thousands of years When the sea level lower than today and coastlines were further out. When it rained. the water would infiltrate into the ground and fill up areas that which are under the sea today.
So when the ice caps started melting during the ending of the last ice age around 20,000 years ago, these areas were later to be covered by oceans, protected from salty seawater by layers of clay and sediment that sit on top of them. This is actually a process similar to aquifers on land on which many rely on drinking water.
In order to extract the water from these underground lakes, you can either use drilling platforms on the ocean, similar to those used for extracting oil, or they could be drilling from an onshore facility.
_______________
Media release: Scientists find vast new freshwater sources under the sea
______________________________









![OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. https://chatgpt.com](https://www.illustratedcuriosity.com/files/media/55136/b1b0b614-5b72-486c-901d-ff244549d67a-350x260.webp)
![OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. https://chatgpt.com](https://www.illustratedcuriosity.com/files/media/55124/79bc18fa-f616-4951-856f-cc724ad5d497-350x260.webp)
![OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. https://chatgpt.com](https://www.illustratedcuriosity.com/files/media/55099/2638a982-b4de-4913-8a1c-1479df352bf3-350x260.webp)








